On this page
Neural Networks
Perceptrons
A perceptron is a 1 neuron (node) model tha can be used to solve certain problems
- Basic examples are modeling: AND gate, OR gate
- Perceptrons work for types of problems in which linearly separable, that is there is linear expression that clearly separates outcomes.
- in other words you can draw a line and the different types (e.g classes) of outcomes are separated
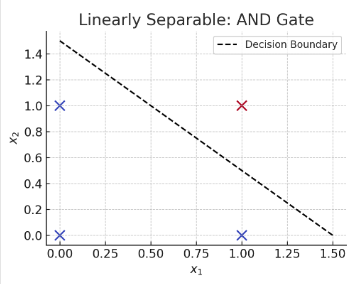
Intuition
- the point of the weighted neuron and bias sum calculation is to define the line that serves as the
decision boundary - all points on one side of the decision boundary are in one class (e.g.
1) and the others are in the other class (e.g.1) - an activation function (threshold function) calculates the output node (which should convert the calculation over or under the decision boundary)
- Process
- configure an architecture (2-2-1) of:
2input neurons (x to be ANDed with y)- a “hidden” layer of
2neurons that serve as the interim output of the weigted sum & bias calculation 1output neuron
- configure an architecture (2-2-1) of:
A perceptron computes a weighted sum of its inputs:
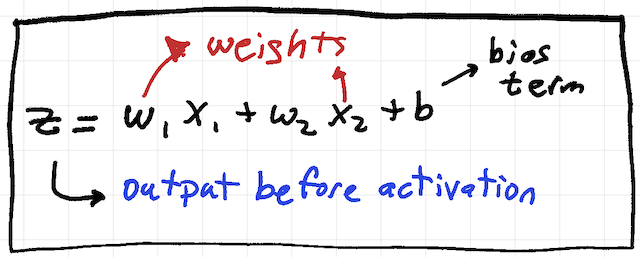
Activation function:

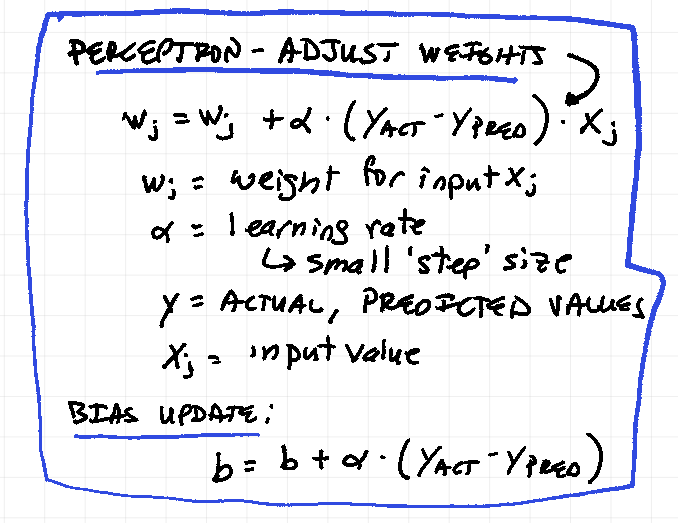
Adjust weights:
Perceptron Python Code
import numpy as np
from scratch.linear_algrebra import add, dot, Vector
# Assume this serves as an activation function
def step_function(x: float) -> float:
return 1.0 if x >= 0 else 0.0
# perceptron_output plays the role of a perceptron
# It takes in a vector of weights, a vector of inputs, and a bias
# It returns 1 if the weighted sum of the inputs is greater than the bias
def perceptron_output(x: Vector, weights: Vector, bias: float) -> float:
# calculate the weighted sum of the inputs x and adds a bias value
calculation = dot(weights, x) + bias
return step_function(calculation)
# Example: AND gate perceptron
weights = [2.0, 2.0] # assign initial weights
bias = -3.0 # assign initial bias
# Test the AND gate perceptron with all possible inputs
print ("Does the logic predict ANDing [1, 1] = 1?", (perceptron_output([1, 1], weights, bias) == 1))
print ("Does the logic predict ANDing [1, 0] = 0?", (perceptron_output([1, 0], weights, bias) == 0))
print ("Does the logic predict ANDing [0, 1] = 0?", (perceptron_output([0, 1], weights, bias) == 0))
print ("Does the logic predict ANDing [0, 0] = 0?", (perceptron_output([0, 0], weights, bias) == 0))
Fast-Forward Neural Networks
- networks that consist of layers of neutrons - each which are connected to the respective neuron in the next layer
- general architecture:
- start with an input layer that passes inputs into the next (hidden) layer
- hidden layers take input from the previous layer (input or interim hidden layer) and perform some calculation (weighted sum, activation) and passes result to next layer
- example activation function: sigmoid function
Fast-Forward Calcuation of the XOR Function
import math
from scratch.linear_algrebra import add, dot, Vector
from typing import List
# define the sigmoid function that will be used as the activation function
def sigmoid(x: float) -> float:
return 1 / (1 + math.exp(-x))
# define the neuron output function
def neuron_output(weights: Vector, inputs: Vector) -> float:
return sigmoid(dot(weights, inputs))
# define the feed_forward function
# the function takes in a neural network (represented as a list (layers) of lists (neurons) that include weights and biases)
def feed_forward(neural_network: List[List[Vector]],
input_vector: Vector) -> List[Vector]:
"""
Feeds the input vector through the neural network.
Returns the outputs of all layers (not just the last one).
"""
outputs: List[Vector] = []
for layer in neural_network:
input_with_bias = input_vector + [1] # add a bias input; assume the bias element is 1
output = [neuron_output(neuron, input_with_bias) # compute the output of each neuron
for neuron in layer]
outputs.append(output) # add to the outputs
input_vector = output # set the output as the input for the next layer
return outputs
# represent a XOR gate network
# NOTE: Basically some guessed or predetermined the correct weights and biases
xor_network = [
[[20.0, 20.0, -30.0], # hidden layer
[20.0, 20.0, -10.0]],
[[-60.0, 60.0, -30.0]] # output layer
]
# test the XOR gate network
test_outputs = feed_forward(xor_network, [0, 0])
# for the XOR(0, 0)
print("Does the logic predict XORing [0, 0] = 0?")
print("The input layer is [0, 0]")
print("The hidden layer is", test_outputs[0])
print("The output layer is", test_outputs[1])
print("The prediction is", test_outputs[1][0])
View this page on GitHub